Interthalamic adhesion
| Interthalamic adhesion | |
|---|---|
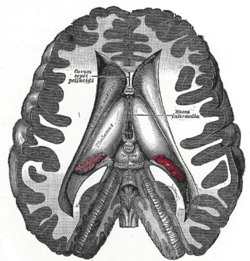 Dissection showing the ventricles of the brain. (Interthalamic adhesion labeled as Massa Intermedia at center right.) | |
 Coronal section of brain through intermediate mass of third ventricle. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Thalamus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | adhaesio interthalamica |
| NeuroNames | 301 |
| NeuroLex ID | nlx_144100 |
| TA98 | A14.1.08.103 |
| TA2 | 5778 |
| FMA | 74869 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The interthalamic adhesion (also known as the massa intermedia, intermediate mass or middle commissure) is a flattened band of tissue that connects both parts of the thalamus at their medial surfaces. The medial surfaces form the upper part of the lateral wall to the third ventricle.
In humans, it is only about one centimeter long – though in females, it is about 50% larger on average.[1] Sometimes, it is in two parts – and 20% of the time, it is absent.[2] In other mammals, it is larger.
In 1889, a Portuguese anatomist by the name of Macedo examined 215 brains, showing that male humans are approximately twice as likely to lack an interthalamic adhesion as are female humans. He also reported its absence, still reported today in about 20% of humans. Its absence is seen to be of no consequence.[2]
The interthalamic adhesion contains nerve cells and nerve fibers; a few of the latter may cross the middle line, but most of them pass toward the middle line and then curve laterally on the same side. It is still uncertain whether the interthalamic adhesion contains fibers that cross the midline – and for this reason, it is inappropriate to call it a commissure.
The interthalamic adhesion is notably enlarged in patients with the type II Arnold–Chiari malformation.[3]
Additional images
[edit]-
Thalamus
-
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere. Medial view. Deep dissection.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Wiley Interscience
- ^ a b Olry, R; Haines, DE (June 2005). "Interthalamic adhesion: scruples about calling a spade a spade?". Journal of the History of the Neurosciences. 14 (2): 116–8. doi:10.1080/096470490910128. PMID 16019656.
- ^ Wolpert, S. M.; Anderson, M; Scott, R. M.; Kwan, E. S.; Runge, V. M. (1987). "Chiari II malformation: MR imaging evaluation". American Journal of Roentgenology. 149 (5): 1033–42. doi:10.2214/ajr.149.5.1033. PMID 3499774.
External links
[edit]- Atlas image: n1a8p6 at the University of Michigan Health System
- Image at Harvard University
- Diagram at csuchico.edu (labeled as Massa intermedia) Archived 2007-01-13 at the Wayback Machine
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.


